Beloved singer and songwriter Jimmy Buffett died on September 1, 2023, after fighting Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Fortunately, Merkel Cell Carcinoma is very rare. If you are concerned about a new, changing, unexplained, or concerning spot on your skin you should have it evaluated by a board-certified dermatologist.
What is Merkel Cell Carcinoma?
Merkel cell carcinoma is a “neuroendocrine” cancer– in the skin this means it is cancer of the cells that are connected to nerves which likely play a role in our touch sensation. But because it is so rare, it is not a very well understood cancer.
How common is Merkel Cell Carcinoma?
Merkel Cell Carcinoma, the kind of skin cancer Jimmy Buffett suffered from according to a statement on his website, is very rare. The American Academy of Dermatology and the Skin Cancer Foundation estimate there are somewhere between 2000 and 3000 new cases of Merkel Cell diagnosed each year in the United States.
Who usually gets Merkel Cell Carcinoma?
Merkel Cell Carcinoma usually occurs in sun-exposed areas in fair-skinned people over 65, and mostly in men. People with weakened immune systems (e.g. chronic forms of leukemia, HIV, transplant patients) are at higher risk of developing Merkel Cell Carcinoma.
What causes Merkel Cell Carcinoma?
The cause of Merkel Cell Carcinoma is not fully understood, but as with most other skin cancers, it is associated with chronic ultraviolet (UV) light exposure. In some cases, a specific virus (Merkel cell polyomavirus) is believed to be a key trigger for developing Merkel Cell cancer.
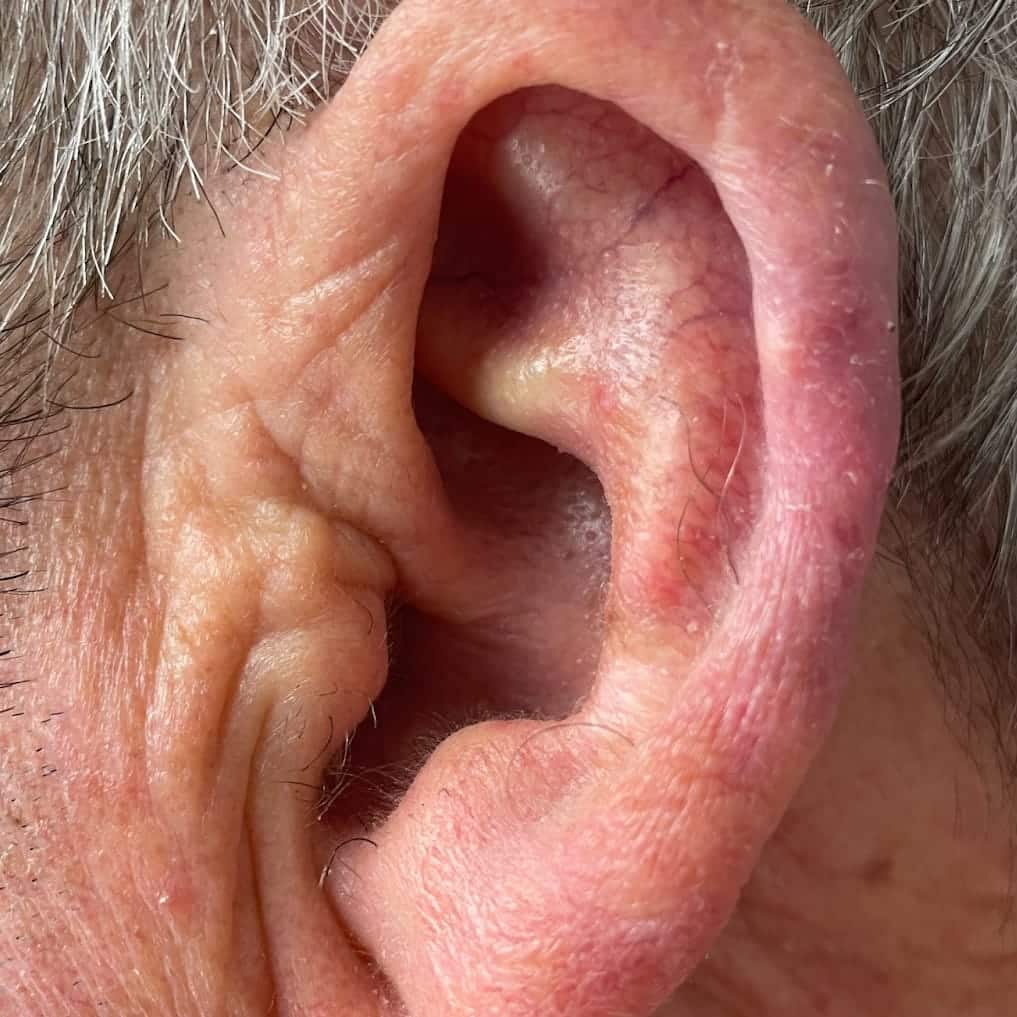
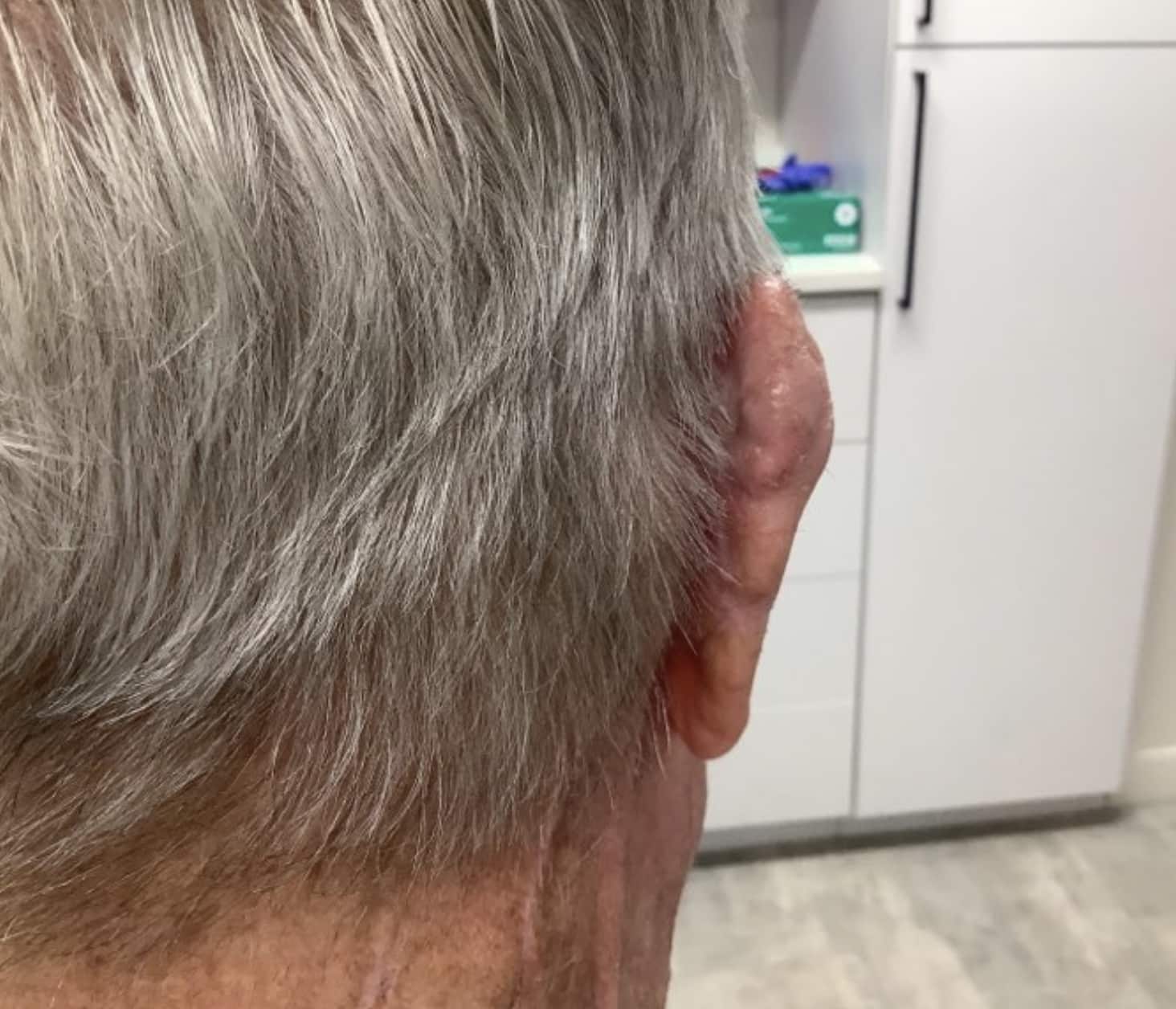
What does Merkel Cell Carcinoma look like?
Merkel Cell Carcinoma is usually noticeable on the skin as an unexplained reddish-purple, quickly growing, non-painful spot or sore. Merkel Cell Carcinoma is usually diagnosed by having a skin biopsy of a suspicious lesion.
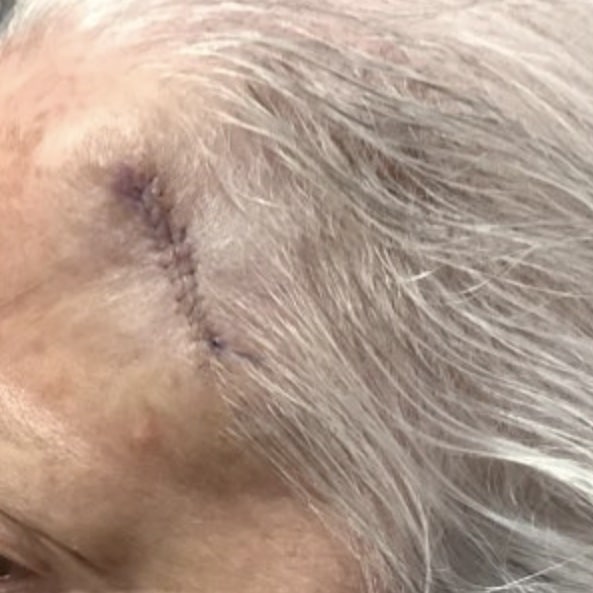
How is Merkel Cell Carcinoma treated?
Once diagnosed, the goal is prompt surgery to get clear margins. A search for the cancer in nearby lymph nodes is almost always performed when this cancer is diagnosed. Unfortunately, it is not uncommon for Merkel Cell Carcinoma to have already spread at the time of diagnosis. As with other cancers that spread to other parts of the body, radiation is sometimes added in as part of the treatment. Merkel Cell Carcinoma doesn’t typically respond well to chemotherapy, but there are other targeted cancer treatments available including medications that capitalize on the body’s own immune system to fight cancer.
What You Can Do ?
Being vigilant about new or changing spots on your skin is very important. You should also have your skin examined by a board-certified dermatologist. Protecting your skin from UV exposure can lower your risk of skin cancer, including the common types of skin cancer such as basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and even melanoma.
You should also practice good sun habits like using broad-spectrum SPF daily, seeking shade, wearing hats and sunglasses, and avoiding intense and prolonged sun exposure.